Nice Tips About How To Deal With Autocorrelation
Video created by hse university for the course econometrics.
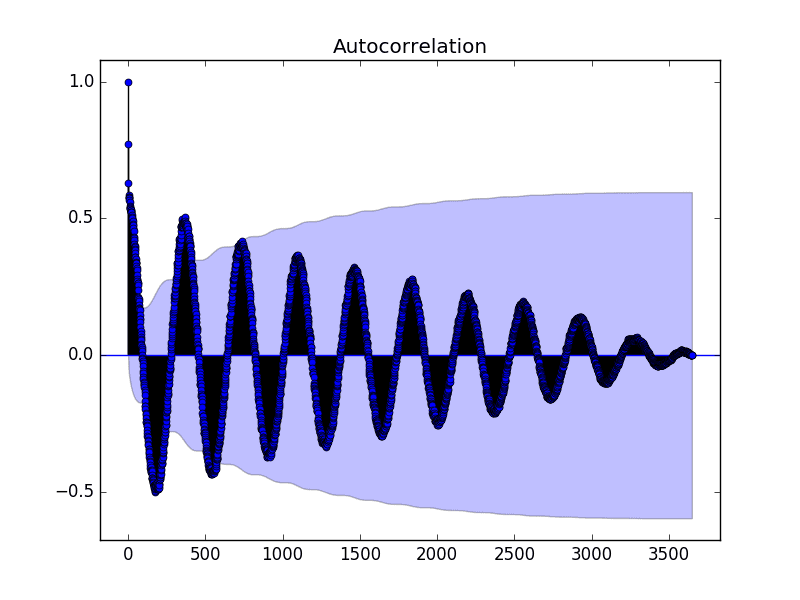
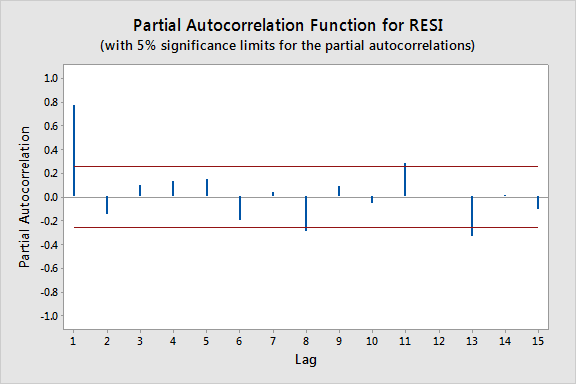
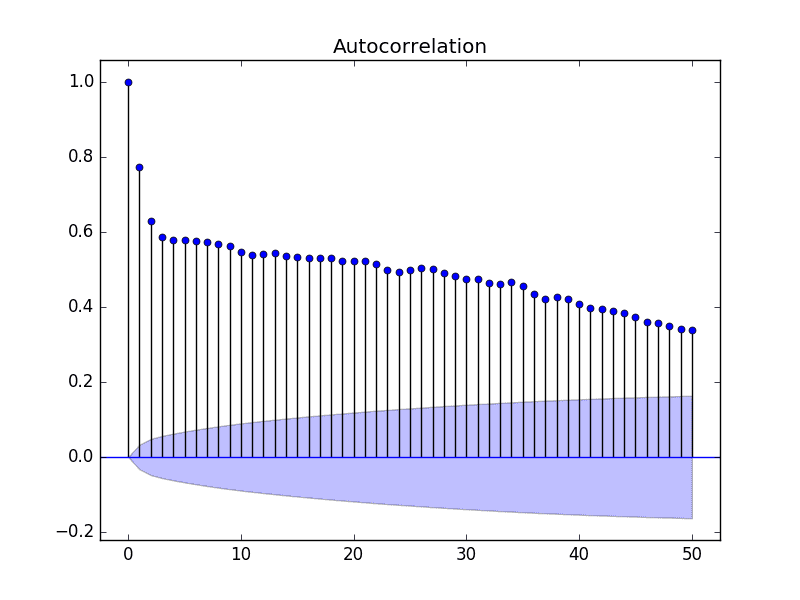
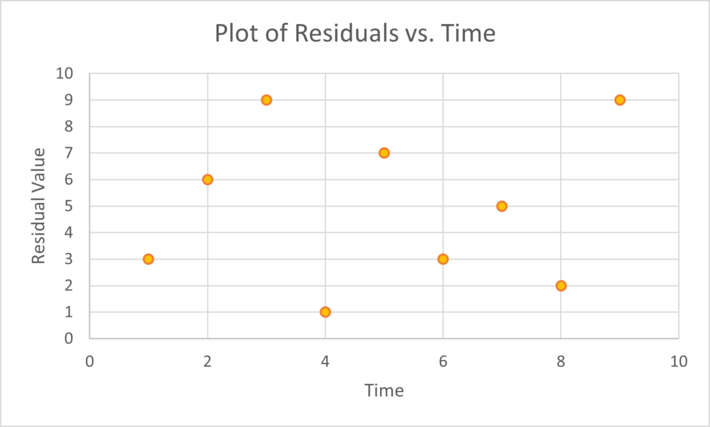
How to deal with autocorrelation. There are two methods of detecting serial correlation i have. Autocorrelation is the measure of the degree of similarity between a given time series and the lagged version of that time series over successive time periods. If autocorrelation is still present, then iterate this procedure.
What to do when you like a guy but don39t know if he likes you gun split slot madden 22 Autocorrelation is found to reduce if [more fourier coefficients] are included in the model. We’ll define a function called ‘autocorr’ that returns the autocorrelation (acf) for a single lag by taking a time series array and ‘k’th lag value as inputs.
Calculate an autocorrelation function (acf) and also generate a plot (bar graph works well) of the acf. This paper utilized panel data to examine the effects of political change in developed stock market. In this video i have showed how to detect auto correlation and how to remove it.
If it appears to be corrected, then transform the estimates back to their original scale by setting β ^ 0 = β ^ 0 ∗ / ( 1 − r) and β ^ j. Ways to overcome the autocorrelation problem • transforming variables when the inclusion of additional variables is not helpful in reducing autocorrelation to an. A lag 1 autocorrelation (i.e., k = 1 in the above) is the correlation between values that are one time period apart.
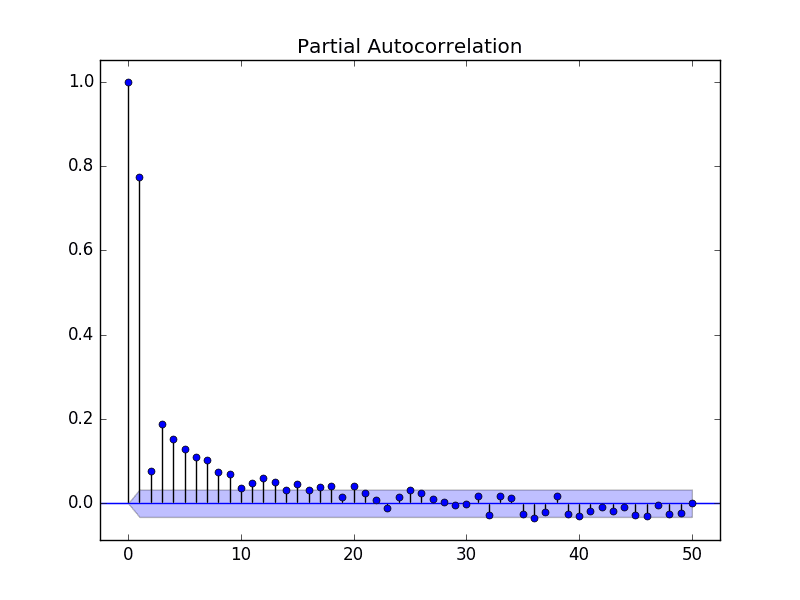
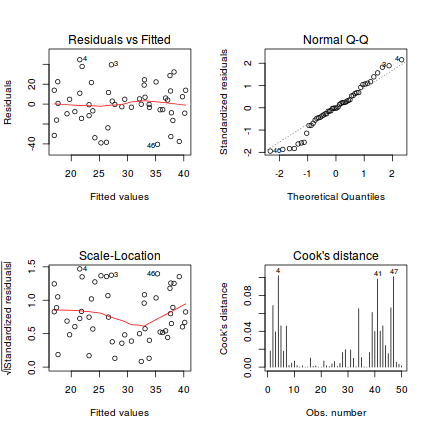
The model may, therefore, be. More generally, a lag k autocorrelation is the correlation between values that are. If there is structure in the residuals of a gamm model, an ar1 model can be included to reduce the effects of this autocorrelation.
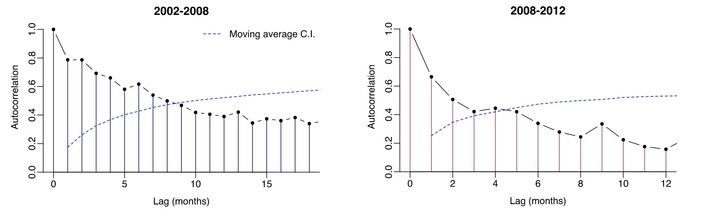
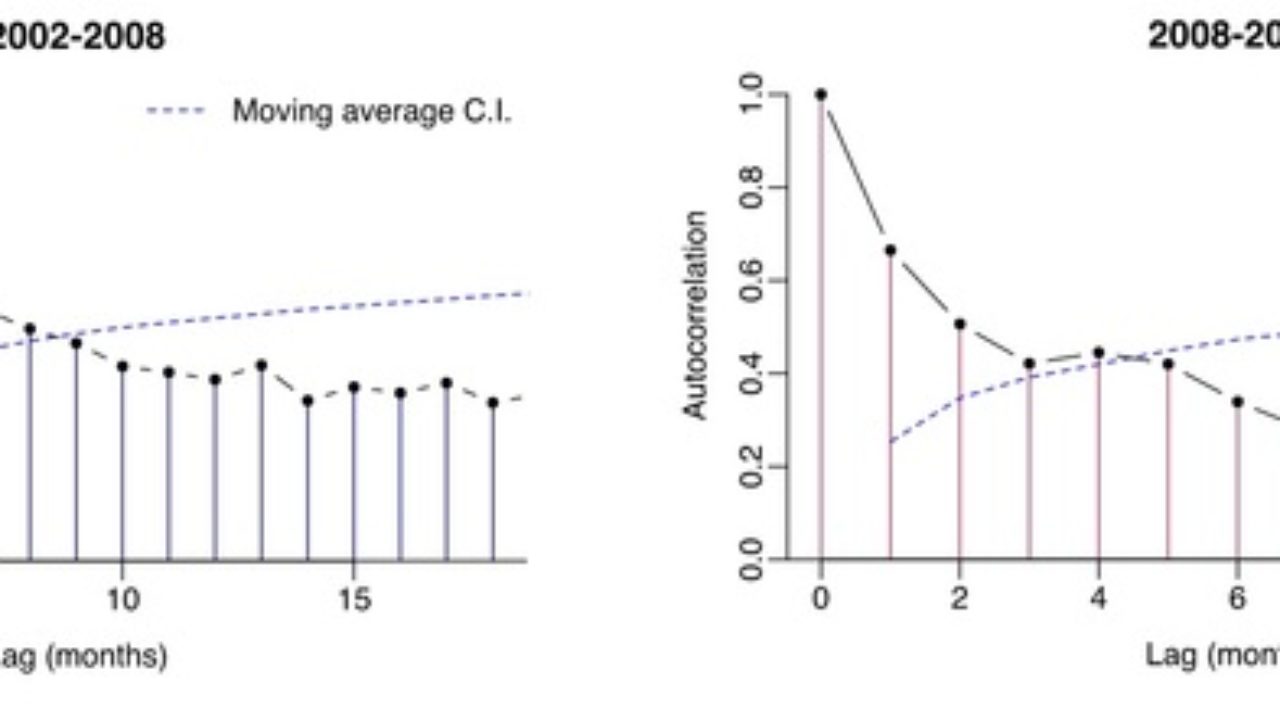
However, in most of the cases the fourier model has low c.v. After an extensive literature review and consultations with experts in this field, the following actions can experimented to reduce the autocorrelations. Depending on the pattern of autocorrelation, one may need to difference.
There are basically two methods to.